The etymology of the word furniture and a brief history of its evolution
It might be interesting for you to know from which culture the word "furniture" entered the Persian language. In this article, we will look at the etymology of the word furniture and examine the evolution of furniture throughout history.
The origin of the word furniture:
In a certain dictionary, the meaning of the word furniture is the set of furniture required for a place. This place can be office, home or any other place. The use of this furniture is used for more comfort and comfort in the conditions of human life, work and recreation.
The French word furniture or meublement, which is rooted in the Latin word mōbilis, which means portable devices and assets, usually refers to practical appliances and devices such as chairs, tables, beds, etc., which have the ability to be carried. In the English language, the word "furniture" is usually used as the equivalent of such tools and equipment, which means the equipment and facilities that cover the space.
Neolithic furniture was sometimes made of stone. Items such as couches, beds, shelves and other objects are examples of these furniture; But today, various materials such as wood, metal, stone, glass, leather, fabric, etc. are used in the production of furniture. Also, different techniques such as carving, covering, painting, inlaying, gilding, painting, or embroidery are used to decorate furniture.
Furniture is a reflection of the evolution of technology and fashion in every culture, and sometimes its practical side is less than its appearance because it is considered as a symbol of social status.
In the last 300 years, attention has been paid to the variety and quantity of furniture, as well as its comfort.
History of furniture:
-
ancient times:
Eastern people in ancient times (Mesopotamia, Iran) inlaid furniture with ivory, gold and other precious materials. Also, to cover these furniture, they used high-quality carpets with silver and gold strips sewn on them.
-
Egypt:
Egyptian people used mats and dyed beech wood to make furniture. This furniture included folding chairs, tables, beds with various shapes and sideboards. The Egyptians decorated their palaces with gold-plated furniture and bright colors.
Egyptian artisans sometimes made furniture from square-shaped wood and decorated it with geometric patterns or carvings, and sometimes used ivory, ebony, and glass paste for decoration. Furniture in the Egyptian era had many forms, including: folding stools, beds that often had curved and inclined backs, chairs, etc. The surface of the seats in this era was flat or concave, and like the frame of the beds, it was tied with ropes or leather strips. The chairs had a decorated footrest and a headrest (made of wood or ivory).
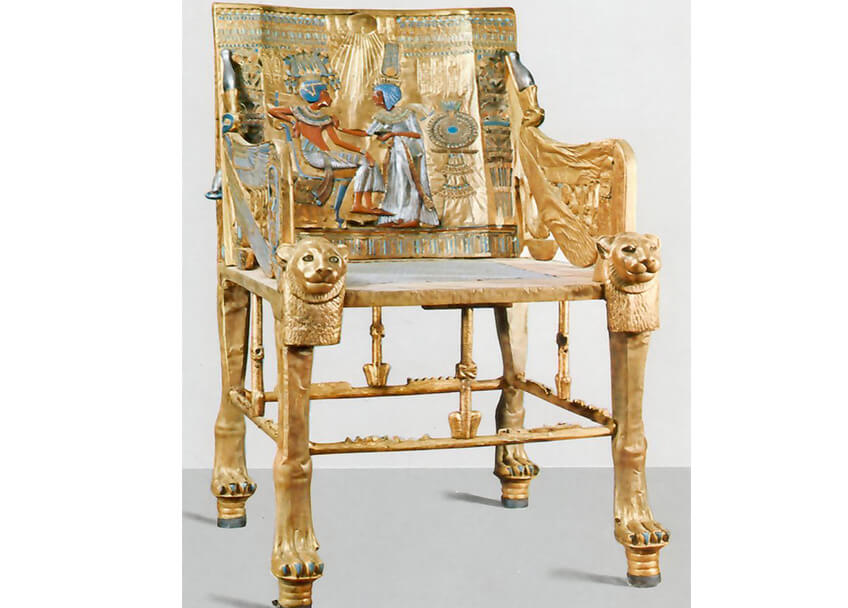

-
Greece:
In the 5th century BC, the Greek people got acquainted with the culture of the East and brought more diverse forms. The Greeks made magnificent beds decorated with precious materials. Beautiful chairs were among the other pieces of furniture that the Greeks made; These chairs had a wide surface and a semi-circular back.
-
Rome:
The Romans further developed the art of the Greeks and decorated their houses with precious marble, mosaics and stucco and used furniture to fill the house.
Roman furniture with a great variety of shapes and materials, especially after the conquest of Greece and Asia Minor, is characterized by attention to comfort and luxury. The raised bed with turn-down legs, which requires steps, has a mattress, cushions and fabric with gold trim. The backs of the beds were in the shape of animal heads with silver inlays. They used special beds to eat. These beds, or today's dining tables, had a bronze base with precious marble or wood tops; It was a bronze or sometimes silver and marble table with supports in the form of a winged griffin.
-
Medieval:
Dagobert's throne remains from the medieval works, which is made of bronze. Other works are related to the 13th century, when furniture became popular again, and items such as wardrobes for clothes, chests as holders of objects, chairs and beds were made.
Furniture made in the 14th and 15th centuries was sturdier and had a frame and panel construction. Among these furniture, we can refer to tables, benches, chairs, buffets, wardrobes, etc.
Renaissance period:
At the beginning of the 15th century, while the rest of Europe was still under Gothic influence, Italy looked to Greco-Roman antiquity for intellectual models and themes to inspire art; Therefore, the architecture and then the furniture were transformed using ancient ornamental words. When the Renaissance began to spread in Europe (at the beginning of the 16th century), many motifs and themes spread thanks to engraving and painting, and decorative techniques diversified. In Italy, these decorations included painting on the panels of chests, cupboards or cabinets.

-
Baroque and Rococo:
In the middle of the 16th century, the Baroque style, synonymous with seduction and movement, appeared in classical art. In the 17th century, baroque furniture, characterized by excessive decoration (even to the detriment of purity of form), reflects the ostentatious taste of wealthy families in various European countries. Aristocrats and bourgeois settled for simpler furniture.
In the first half of the 17th century, France depended on the manufactures of its neighbors, especially for cabinets and decorated tables and chairs. After that, France became independent in furniture production with the creation of the royal furniture factory and the famous cabinet making workshop of Andre Charles Boule. During this period, great cabinet makers such as Pietro Pifetti in Turin, the brothers Spindler and Hoppenhaupt in Berlin, Thomas Chippendale in London, Charles Crescent, van Riesenburgs, Antoine Robert Gaudreau, Jean-François Aubin in Paris They created furniture that was very popular in its time.
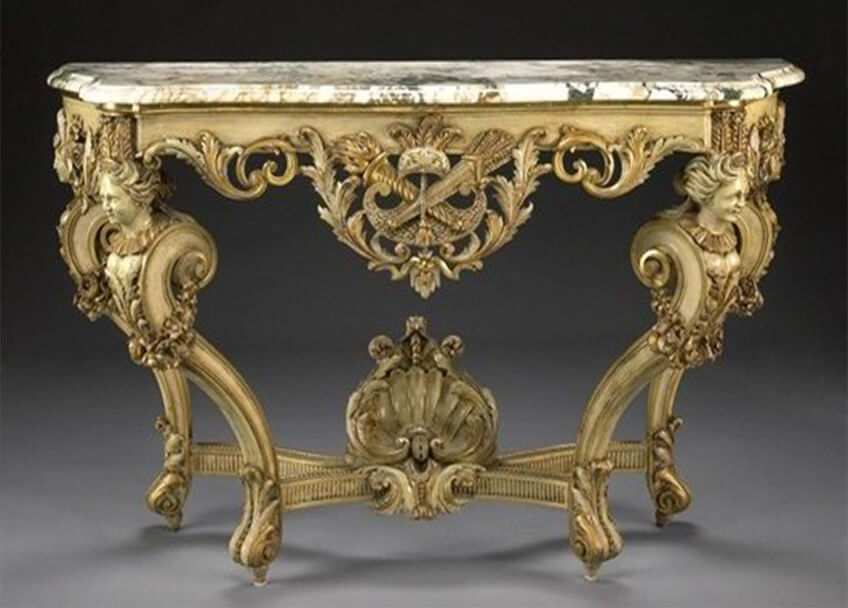

-
Neoclassical:
Around 1760, a reaction to the Rococo developed throughout Europe - opposed to classical austerity - but its main idea was a return to the past. Furniture design in this period changed from the wavy curved shapes of Rococo to straight and symmetrical lines. In the neoclassical style, mahogany wood was used more and bright colors were more popular.
19th century:
19th century furniture includes three periods of empire, eclectic and industrial production. The imperial style was inspired by the architectural style of Rome, Greece and ancient Egypt and was very impressive and luxurious. With Napoleon's exile, his grand imperial style gradually lost its appeal.
In the eclectic period, all the styles of the previous periods became popular in a short period of time. This trend inclined the designs towards Indian, Turkish, Persian, Chinese and Japanese styles.
Inspired by the cane-making technique and starting from Biedermeier's furniture aesthetics, Michael Tonet, a German living in Vienna, revolutionized furniture around 1840, leading to even greater improvements.
He basically made chairs from a small number of components: beech wood, softened and pliable, then bent and shaped in molds, and finally assembled with bolts and nuts. Thanks to their elegance, strength and moderate price, these chairs found their place in Viennese palaces as well as among bourgeois or cafes: chairs with different types of backs, rocking chairs, office chairs, small tables, shelves and beds, among other furniture in production. There are industries that were mass produced in factories.
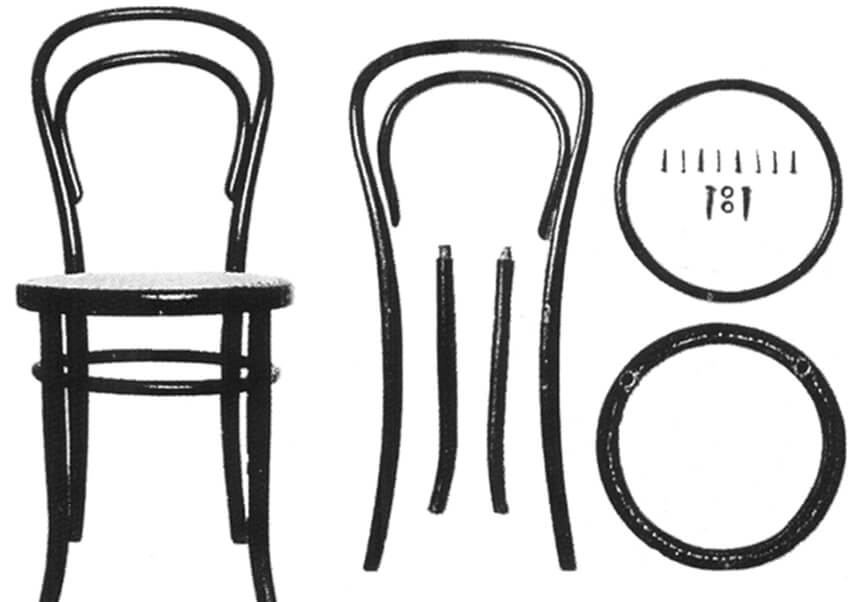

-
Beginning of the 20th century:
This period is also divided into two categories: new art (Art Nouveau) and decorative art (Art Deco). Architect Hector Guimard declared in 1899, "We must always look for our ideas in nature," thus defining the new aesthetics of the Art Nouveau movement due to the influence of Japonism and Symbolism. The creators of this style are seduced by the linear features of the plant and its expression of an organic force; Therefore, in furniture, the base is generally made of curves that are stretched out and open, and the plan of the furniture is often curved, the forms are fluid, and finally, the decorations in the art nouveau style are prominent and well integrated with the structure.
Art Deco was considered an unconventional style due to the use of non-functional decorations such as circle shapes, zigzag shapes, stair steps and solar panels in furniture. In Art Deco furniture design, the use of rich and dignified colors and expensive materials such as ebony wood, ivory, stone and the like were popular.

-
Modern style furniture:
This style, which peaked in the second decade of the 20th century, appeared in different European countries in different forms and by many designers. Functionalism and the use of new materials and methods in line with mass production were the characteristics of this style, and the goal of furniture design was to produce a durable, beautiful and efficient product. Works designed by Frank Lloyd Wright, Mies van der Rohe and Le Corbusier are included in this style.

Materials commonly used in modern period furniture included metal, glass and concrete. These materials were mass produced in the factory.
FAQ
The word "meublé" is a French word derived from the Latin root "mōbilis" and means portable furniture.
The oldest remaining furniture is related to ancient times and civilizations of Mesopotamia and Iran.
Archaeological excavations show that the first and oldest piece of furniture in Iran was a stool that was made in the Elamite period. After that, the bed is the most used and the oldest piece of furniture made in the history of Iran.







Share